扁桃体ー視床下部ー延髄回路と運動限界の関係についてのレビュー論文が『Frontiers in Physiology』誌に掲載されました
2026/01/13
これまでに研究室から出版された運動限界に関する論文:
- Kim et al., Neuroscience, 2020
- Tsukioka et al.,Neuroscience, 2022
- Ezure et al.,JPFSM,2023 を中心にまとめたレビューが『Frontiers in Physiology』誌に掲載されました。

Yamanaka K, Kim J, Tsukioka K, Ezure S, Ichihara H, Pham LT, Waki H.
Amygdala–hypothalamus–brainstem circuits underlying cardiovascular responses associated with the limits of
high-intensity endurance exercise.
Front.Physiol. 2026 12 Jan;16. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70298.
Sec. Exercise Physiology, Physiological Aspects of Marathon Running, Volume II
文京区教育だより『きあら』にコラムが掲載されました
2026/01/11
文京区教育だより『きあら』に健康推進についてのコラムが掲載されました。
「健康・体力アップ!のヒント 第7弾・「わかっているけどなかなかできない…」運動意欲を高めるヒント」
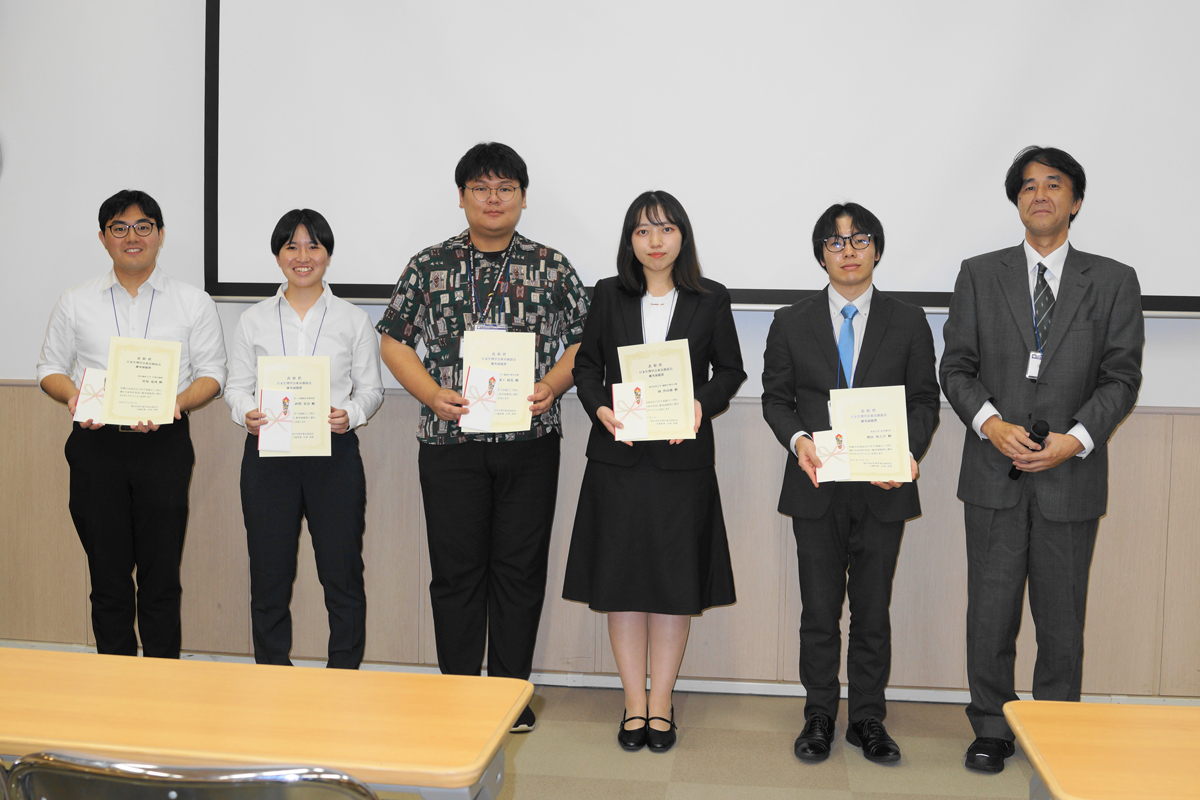
第255回生理学東京談話会で発表を行いました。M1の砂間さんが若手の「優秀演題賞」を受賞しました🌸
2025/10/07
10月4日(土)に順天堂大学にて開催された第255回生理学東京談話会(関東・東京地区地方会)で、金芝美さん、Pham Thuy Linhさん、砂間栞奈さんが口頭発表を行いました。
砂間さんが若手の「優秀演題賞」を受賞しました!おめでとうございます🌸

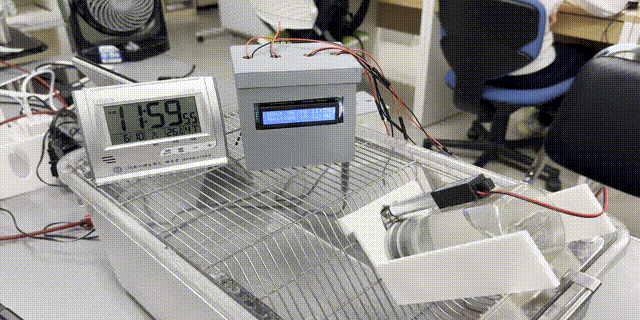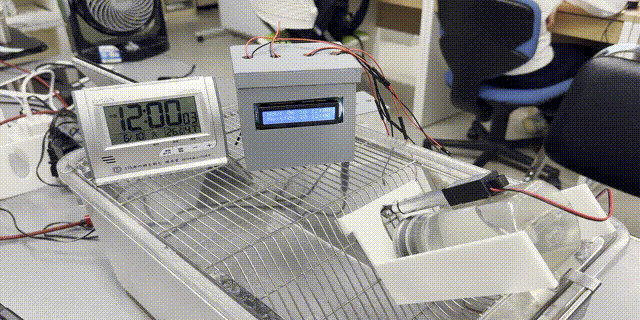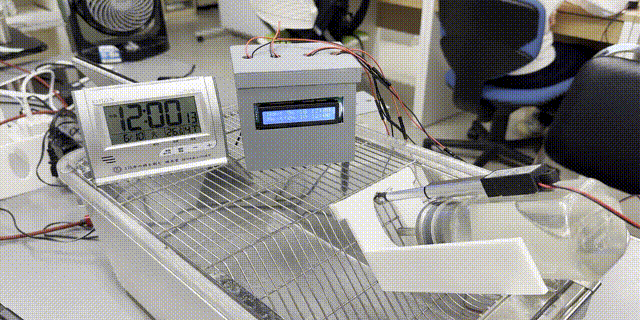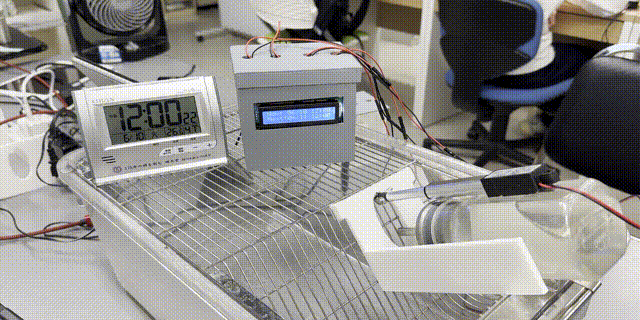
「【研究資料】低コストArduinoベースの動物ケージ用自動給水制限装置」が『順天堂スポーツ健康科学研究』誌(紀要)に掲載されました
2025/07/22
『順天堂スポーツ健康科学研究』誌に、大学院生(M1)の砂間さんを筆頭著者としたArduinoと3Dプリンタを用いた低コストで実現可能な動物ケージ用自動給水制限装置についての研究資料が公開されました。
砂間栞奈、和氣秀文、山中航
低コストArduinoベースの動物ケージ用自動給水制限装置
A low-cost Arduino-based system for automatic water restriction in animal cages
順天堂スポーツ健康科学研究 2025 Jul 22;16(1):1-6.
ソースコード・3Dモデルデータ等はGitHubで公開しています。
妊娠時の血圧上昇における運動の効果について報告した論文が『Physiological Reports』誌に掲載されました
2025/04/09
『Physiological Reports』誌に妊娠時の血圧上昇における運動の効果について報告した論文が掲載されました。筆頭著者の小林徹さん(医学研究科・産婦人科学講座)の学位論文になります。おめでとうございます🌸
Kobayashi T, Pham LT, Kobayashi M, Yamanaka K, Itakura A, Waki H.
Inhibitory effect of exercise on elevated blood pressure and fetal growth restriction during pregnancy in Dahl salt-sensitive rats.
Physiol Rep. 2025 Apr;13(7):e70298. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70298.
PMID: 40205775; PMCID: PMC11982524.
(2025-04-09)
『標準生理学 第10版』の「第14編 環境と生体:第61章 運動と体力」を和氣教授が執筆しました
2025/04/07
『標準生理学 第10版』の「第14編 環境と生体:第61章 運動と体力」を和氣教授が執筆しました。『標準生理学 第10版』は2025年4月7日刊行です。
研究室の新メンバーとして、Liu Yannaさん、韓承我さん、Phung Son Haiさん、遠藤大和さん、砂間栞奈さん、瀧澤咲和さん、林ひよりさん、堀内瞳冶さんが加わりました
2025/04/02
協力研究員として刘彦娜(Liu Yanna)さん、ポスドクとして韓承我(Han Seungah)さん、大学院博士後期課程にPhung Son Haiさん、大学院博士前期課程に、遠藤大和さん、砂間栞奈さん、瀧澤咲和さん、林ひよりさん、堀内瞳冶さんが新しく加わりました。
よろしくお願いします。
Juntendo Scopeに金箱さんの座談会企画の続報が掲載されました
2年前の座談会企画の続報で、金箱さんがインタビューされました。
2025/03/21
2年前、あの座談会で語った夢と今—研究と向き合った日々の先に~運動開始のタイミングと心周期の関係性について~
↓2年前の記事 (2023/05/19)
【座談会企画】スポ健で見つけた私の学び 卒業研究を振り返る
ハイパフォーマンス・トランスレーショナル・リサーチ拠点(HPTRC)の活動がGood Health Journalに掲載されています
ハイパフォーマンス・トランスレーショナル・リサーチ拠点(HPTRC)の活動がGood Health Journalに掲載されています。
■ 順天堂 - Good Health Journal
2025.03.05 脳、腸内細菌、厚底シューズ、AI体操―。新たな発想でトップアスリートをさらなる高みに押し上げる研究拠点「HPTRC」



